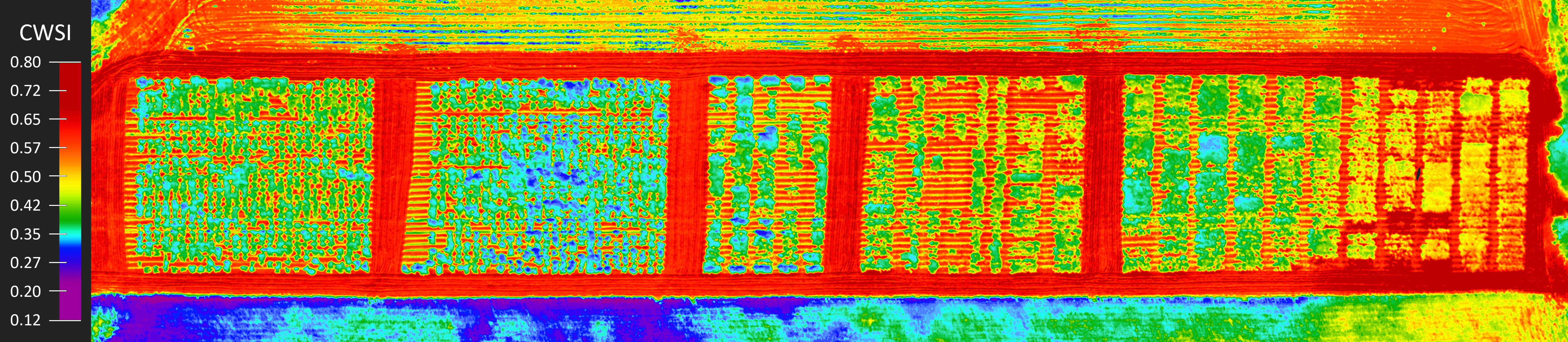
Drone-Mounted Thermal Camera Measurements of a Landscape Surface
The orthothermogram on the left is composed of 1500 separate thermograms acquired by the Workswell WIRIS ProSc thermal camera and composed in Pix4Dmapper software. The orthothermogram maps an area of approximately 5 hectares (50,000 m2) and was taken by a drone during two separate flights (flight time 50 m) from a height of 70 m.
 Move the Cursor over the image to zoom
Move the Cursor over the image to zoom
Drone-mounted thermal cameras can be used to measure various properties of a landscape surface. These cameras capture infrared radiation emitted by objects and convert it into a visual representation of temperature differences, which can provide valuable insights into the thermal characteristics of the landscape. Some common measurements that can be obtained using drone-mounted thermal cameras include:
Surface temperature: Thermal cameras can provide accurate measurements of surface temperatures of various objects and materials on the landscape, such as soil, vegetation, water bodies, and built structures. This information can be used to assess the thermal behavior of different land cover types, detect temperature anomalies, and monitor changes in surface temperature over time.
Thermal gradients: Drone-mounted thermal cameras can help identify areas with significant temperature gradients, which can indicate variations in heat dissipation or accumulation across the landscape. This information can be useful in studying microclimates, identifying areas prone to frost or heat stress, and understanding thermal dynamics within an ecosystem.
Water body temperature: Thermal cameras can measure the temperature of water bodies, such as lakes, rivers, and ponds, which can provide insights into their thermal stratification, circulation patterns, and ecological conditions. This information is valuable for studying water quality, aquatic habitat, and thermal dynamics of aquatic systems.
Vegetation health: Thermal cameras can detect temperature differences in vegetation, which can be used as an indicator of vegetation health. Healthy vegetation typically has lower temperatures due to efficient water uptake and transpiration, while stressed or diseased vegetation may exhibit higher temperatures due to reduced water uptake or impaired physiological processes. Drone-mounted thermal cameras can be used to monitor vegetation health, detect stress or disease in crops, forests, and other vegetation types.
Urban heat island effect: Drone-mounted thermal cameras can help assess the urban heat island effect, which refers to the phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures compared to surrounding rural areas. Thermal cameras can detect temperature differences between urban and non-urban areas, which can provide insights into the extent and intensity of urban heat islands and help inform urban planning and design strategies to mitigate the heat island effect.
Wildfire monitoring: Drone-mounted thermal cameras can be used for early detection and monitoring of wildfires. Thermal cameras can detect the heat signature of fires, allowing for early detection and tracking of fire spread. This information can be used for fire management and mitigation efforts, such as identifying fire fronts, monitoring fire behavior, and assessing fire impacts on the landscape.
Overall, drone-mounted thermal cameras can provide valuable measurements of landscape surface properties, allowing for a better understanding of thermal dynamics, environmental conditions, and ecological processes in various landscapes.
